Will Cyber Security Be in Demand in the Future?
Nowadays, businesses, governments, and individuals depend on secure systems to protect sensitive data, financial assets, and operational continuity. This makes the question, “Will cyber security be in demand in the future?”, not just relevant- it’s critical for career planning, corporate strategy, and long-term technology investments. As cyber threats grow in complexity and frequency, cyber security has become a key foundation to modern business and technology infrastructure.
Now keep in mind, cyber security is a subfield of information security that focuses on the technical controls involved in defending computer systems and networks. Here’s a breakdown on the difference between cyber security and information security.
Current Trends Driving Cyber Security Demand
1. Increasing Cyber Threats
Cybercrime has evolved from opportunistic attacks to highly sophisticated, organized operations. According to Cybersecurity Ventures, global cybercrime costs are expected to reach $11 trillion annually by 2025, up from $6 trillion in 2021. Threats include ransomware, phishing attacks, and supply chain breaches.
The rise of malware-as-a-service (MaaS) platforms has lowered the technical barrier for attackers, allowing even inexperienced criminals to launch sophisticated attacks. Businesses must invest in robust cyber security to defend against these increasingly accessible threats.
2. Digital Transformation and Cloud Adoption
Digital transformation initiatives are accelerating across industries, from healthcare and finance to manufacturing. As organizations shift workloads between their own servers and cloud environments and integrate IoT devices, they expand their attack surface.
This creates demand for professionals skilled in cloud security, network security, and secure software development, ensuring that critical systems remain resilient. The ISC² Cybersecurity Workforce Study identifies cloud computing security as a top skills gap, reflecting urgent market demand.
3. Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
Governments are imposing stricter cyber security regulations. Laws like GDPR in Europe, HIPAA in the U.S., and the NIS2 Directive across the EU require organizations to protect sensitive data and report breaches.
Regulatory pressures drive companies to hire cyber security experts not only to defend their networks but also to ensure compliance. According to CyberSN, 40% of organizations report that regulatory requirements directly influence their hiring practices.
4. Integration into Business Strategy
Cyber security is no longer just a technical function; it is increasingly recognized as a strategic business enabler. Organizations are embedding security into product design, operations, and customer engagement strategies.
The World Economic Forum ranks cyber security skills as one of the fastest-growing skill categories worldwide, second only to AI and big data expertise. Professionals with both technical and strategic expertise are in high demand.
Real-World Applications of Cyber Security
1. Financial Services
Financial institutions are prime targets due to the high value data and money they manage. Cyber security professionals help safeguard transactions, protect customer information, and prevent fraud. Threat detection and real-time monitoring are essential in this sector, with many AI-powered tools emerging in the market.
2. Healthcare
The healthcare industry manages sensitive patient information and increasingly relies on connected medical devices. Cyber security ensures compliance with HIPAA and prevents breaches that could compromise patient care. As telemedicine and IoT-enabled devices expand, healthcare security expertise becomes even more critical.
2. Critical Infrastructure
Industries such as energy, transportation, and telecommunications rely on secure networks to maintain essential services. Cyber attacks on these sectors can have severe economic and safety consequences. Professionals in network security critical infrastructure protection and operational technology (OT) security are highly sought after.
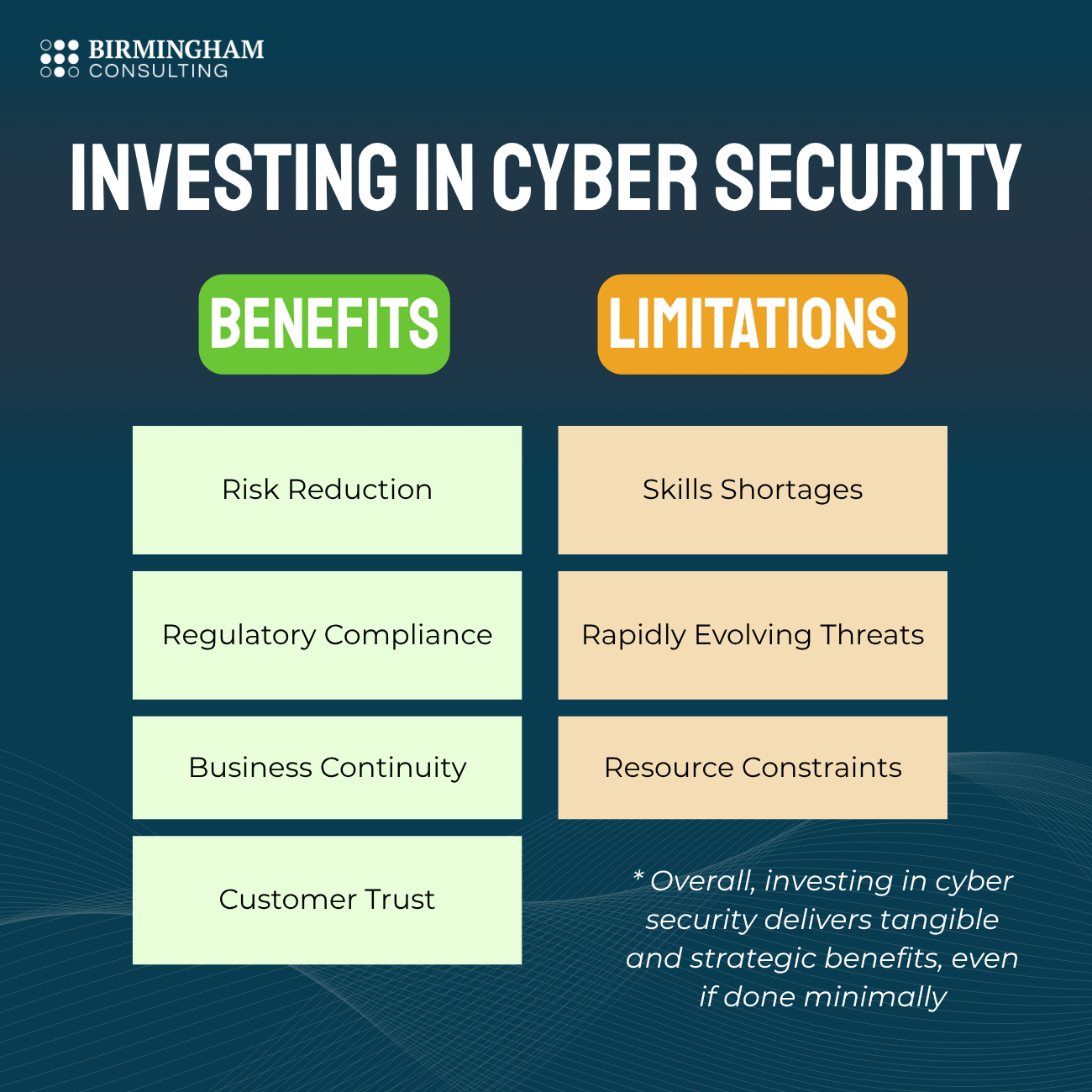
Benefits of Investing in Cyber Security
Investing in cyber security delivers tangible and strategic benefits:
- Risk Reduction: Reduces the likelihood of financial and operational losses due to cyber attacks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps organizations meet legal requirements and avoid fines.
- Business Continuity: Ensures operations are maintained during and after a security incident.
- Customer Trust: Enhances reputation by protecting sensitive data and demonstrating reliability.
These benefits highlight why organizations continue to increase cyber security budgets and staffing levels, further driving demand for skilled professionals.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite its importance, cyber security faces some limitations:
- Skill Shortages: There is a global shortage of qualified cyber security professionals. ISC² estimates a workforce gap of 3.4 million in 2025.
- Rapidly Evolving Threats: Cyber threats evolve faster than many organizations can respond, requiring continuous learning and system updates.
- Resource Constraints: Smaller organizations may struggle to invest in advanced security measures, creating uneven protection levels across industries.
Recognizing these challenges is critical for both organizations planning cyber security strategies and professionals entering the field.
Future Outlook for Cyber Security Demand
1. Exponential Growth in Job Opportunities
Thanks to ongoing traditional threats and the rapid rate of AI adoption, the demand for cyber security professionals is projected to grow significantly. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, information security analyst roles are expected to grow by 35% between 2021 and 2031, much faster than the average for all occupations.
Roles in cloud security, threat intelligence, security architecture, and incident response are expanding as organizations adopt proactive security postures.
2. Emerging Technologies Driving Demand
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered tools are becoming effective at detecting anomalies, predict threats, and automate response processes. Professionals skilled in AI-enhanced security, including human oversight, are increasingly valued.
- Zero Trust Security Models: These models require rigorous verification of users and devices, creating a demand for architects and administrators capable of implementing and maintaining these frameworks.
- Blockchain Security: As blockchain adoption grows beyond cryptocurrency, experts who understand its security applications are needed.
3. Industry-Specific Demand
- Telecommunications: With both existing and future mobile networks, telecom companies prioritize network security.
- Financial Services: Regulatory compliance and digital banking innovations require constant security oversight.
- Healthcare: Telehealth and connected devices necessitate ongoing cyber security investments.
- Government and Critical Infrastructure: National security concerns make cyber security a priority, offering stable, high-demand career opportunities.
- Automotive: As vehicles become connected and autonomous, cyber security roles in product security and safety-critical systems are growing.
Actionable Insights
For professionals considering a cyber security career or organizations planning their staffing strategy:
- Develop Hybrid Skills: Combine technical expertise with business acumen to maximize career potential.
- Specialize in High-Demand Areas: Focus on AI, cloud security, zero trust frameworks, or threat intelligence.
- Continuous Learning: Keep up with evolving threats and security tools.
- Certifications Matter: Industry-recognized certifications like CISSP, CISM, or CISA enhance employability.
- Adopt Proactive Security Strategies: Organizations should integrate security into operations and culture rather than treating it as a reactive measure.
Conclusion
So, will cyber security be in demand in the future? The evidence is clear: cyber security will remain one of the fastest-growing fields for the foreseeable future. Rising cyber threats, expanding digital infrastructures, regulatory pressures, and the strategic importance of security all contribute to sustained demand for skilled professionals.
For individuals, this means abundant career opportunities across industries. For organizations, it underscores the necessity of investing in robust cyber security measures and talent to safeguard operations, data, and reputation. In short, cyber security is not just a temporary trend—it is a permanent, critical component of the modern digital landscape.
Sources:
- Cybersecurity Ventures: Cybercrime Costs – https://cybersecurityventures.com/cybercrime-damages-6-trillion-by-2021/
- ISC² Cybersecurity Workforce Study 2024
- World Economic Forum: Future of Jobs Report 2025 – https://www.weforum.org/reports/future-of-jobs-report-2025
- CyberSN U.S. Cybersecurity Job Posting Data Report
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics: Information Security Analysts Job Outlook